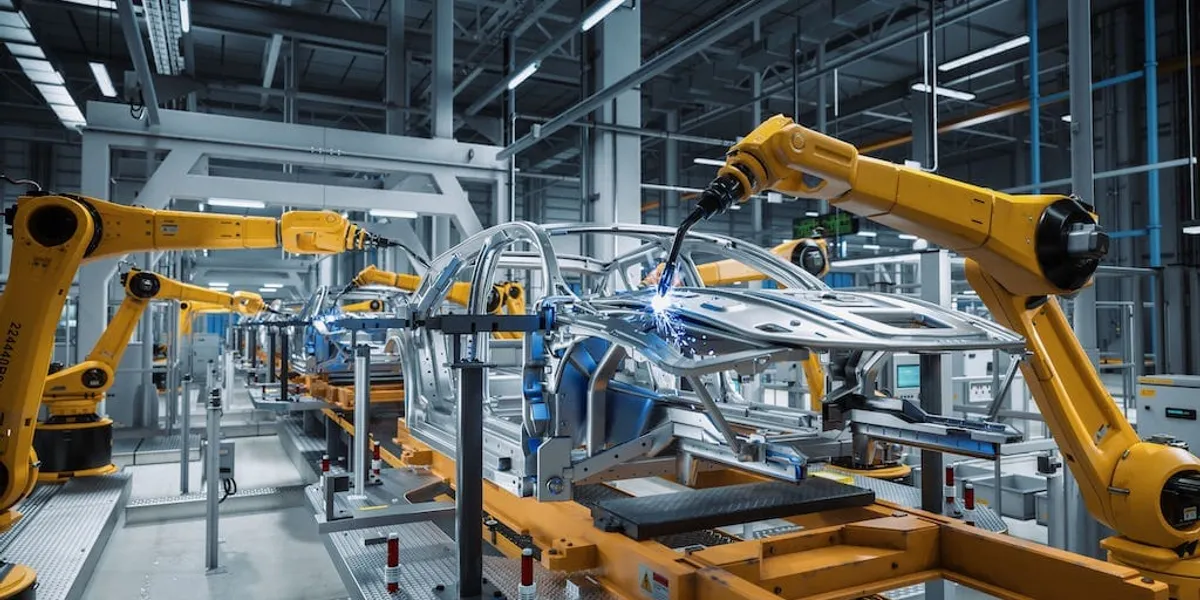
With the rapid growth of technology, it has now influenced different aspects of people's lives and various industries (Calimanu, 2023). Automation and robotics are just some of the many commonly used technologies nowadays, but they will be the focus of this discussion. So, what roles do they exactly play in reshaping the workforce?
Before answering those questions, let us foremost know what automation and robotics are, as they are the center of the discourse.
What is Automation?
Automation is the process of using any technology or machine to do human tasks or finish them faster than it usually takes for a person (Groover, 2023). Groover further mentioned that it only requires three things to work:
- A Power Source;
- Feedback Controls; and
- Machine Programming
It requires little to no user involvement (Rouse, 2023). Thus, it generally aims to ease and modernize the usual easy-to-complicated jobs people do.
Examples of Automation
Some examples of automation cited by Groover (2023) are the following:
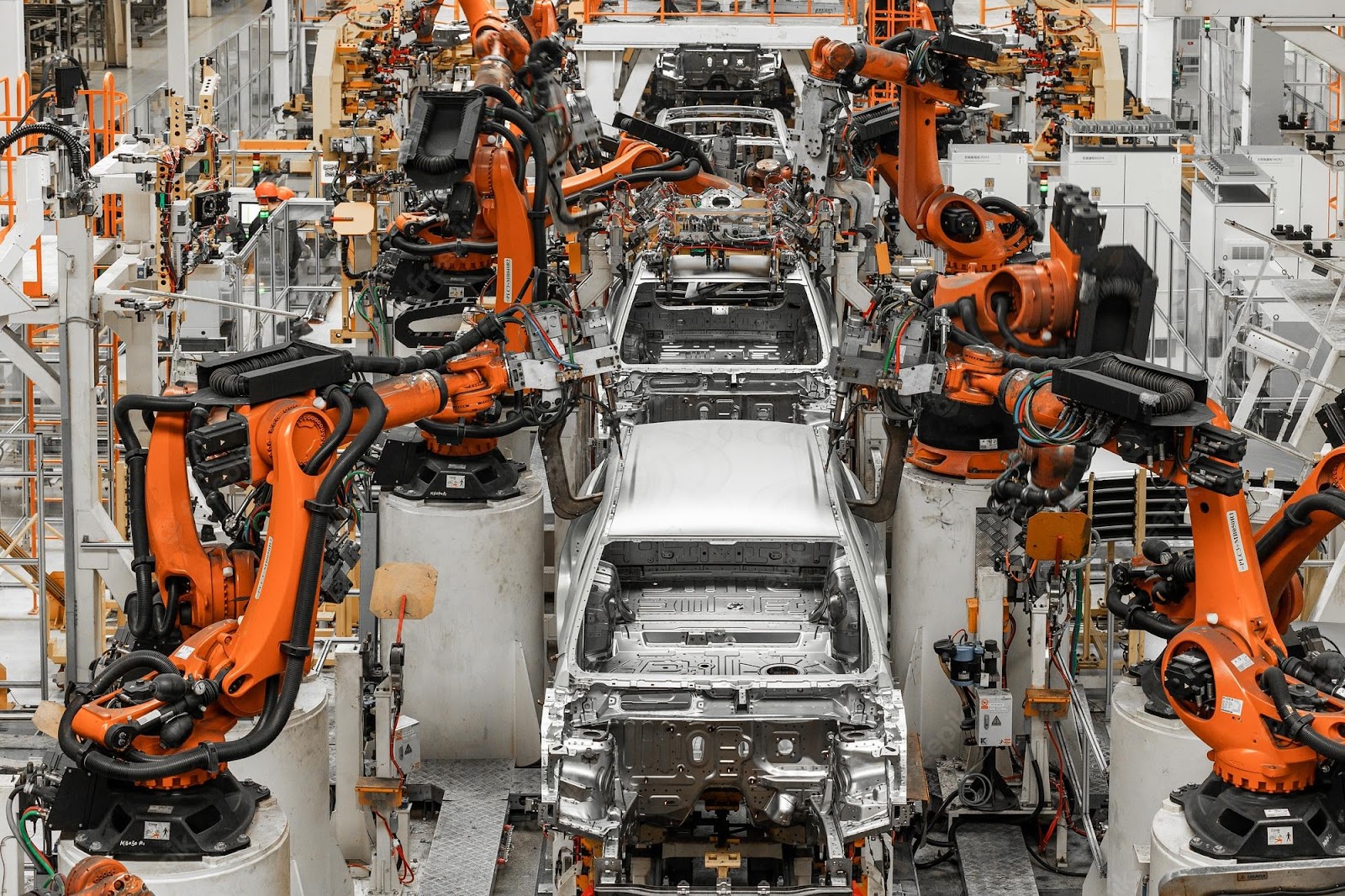
Automated Production Lines in Factories
Automated Numerical Control
Robots in Manufacturing
Automation in Communication
Automation in Transportation
Automation in Service Industries
These are factories divided into different stations of machines doing varying tasks repeatedly to create a product. Here, machines in each station pass their products to the subsequent station.
These can be digital or physical machines
programmed to perform specific actions when they receive commands in numbers or symbols.
These can be the usage of programmed machines to perform tasks in a production process, like handling materials or products.
This is the usage of technology to relay audio and visual messages to others more conveniently and faster.
These are innovations added to the transportation system to enable people to book or pay for their rides without talking to an agent. They can also be the actual innovations applied to vehicles to improve their user experience.
What is Robotics?
Robotics is a field of study involved in designing, constructing, and utilizing machines to move, act, or perform human tasks (The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica, 2023); such machines, which resemble humans capable of moving on their own and in a complex way, are called robots (Merriam-Webster, n.d.). Basically, it is the study or science of robots.
Examples of Robotics
As mentioned, robotics technically focuses on the development of robots, and there are many prominent areas of study under its scope. Some areas of study for robotics at The University of Michigan (Michigan Robotics, n.d.) include:
Manufacturing Robots
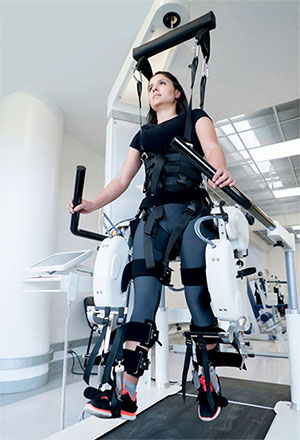
Rehabilitation Robotics
Large-scale production processes often incorporate heavy-duty robots that allow speedy and efficient production of certain items. Industrial robots may be some of the most familiar in the field.
Why are Automation and Robotics Considered Disruptive Technologies?
Having established the basic concepts of Automation and Robotics, we then explore how these can shake up other fields and sectors.
Automation
Automation stands as a disruptive technology as it reshapes industries and the economy. The effect of automation is felt across a spectrum of sectors, and societies at large. Beyond manufacturing processes, it expands to other technologies such as software, hardware, and systems.
For this discussion, we focus on how it alters the traditional archetypes of work through challenging pre-established business models. With this, socio-economic patterns and traditions change to cope with the latest trends.
Looking into this further, we consider how automation disrupts the workforce in various aspects.
Situations Where Automation Disrupts The Workforce
Education
Learning Management Systems
LMS platforms automate the management of educational courses, including content delivery, student enrollment, and assessment tracking. These systems streamline administrative tasks for educators and facilitate online learning.
Source: UPOU MyPortal
Source: Google Workspace
Online Assessment Tools
Online assessment tools enable educators to efficiently create, administer, and grade tests, providing benefits like instant feedback and remote assessment. This shift requires educators to adapt to new technologies, emphasizing data interpretation to understand individual student performance and identify areas of strength or weakness.
Source: Google Forms
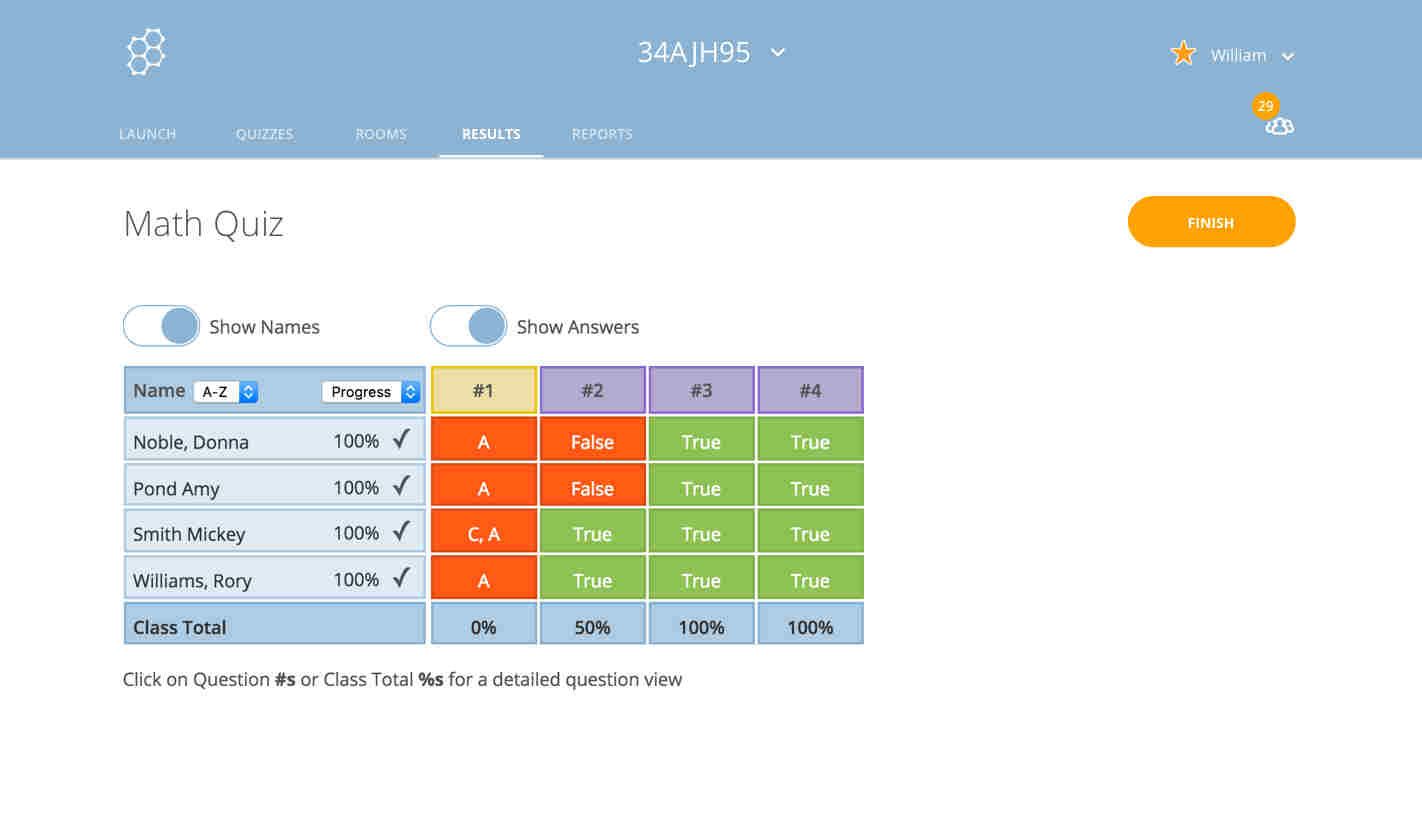
Source: Socrative
Food Service
Self-Service Kiosks
Allow customers to place orders, customize their meals, and make payments without interacting with a cashier. This reduces the need for front-of-house staff to take and process orders, reshaping the roles of traditional cashiers.
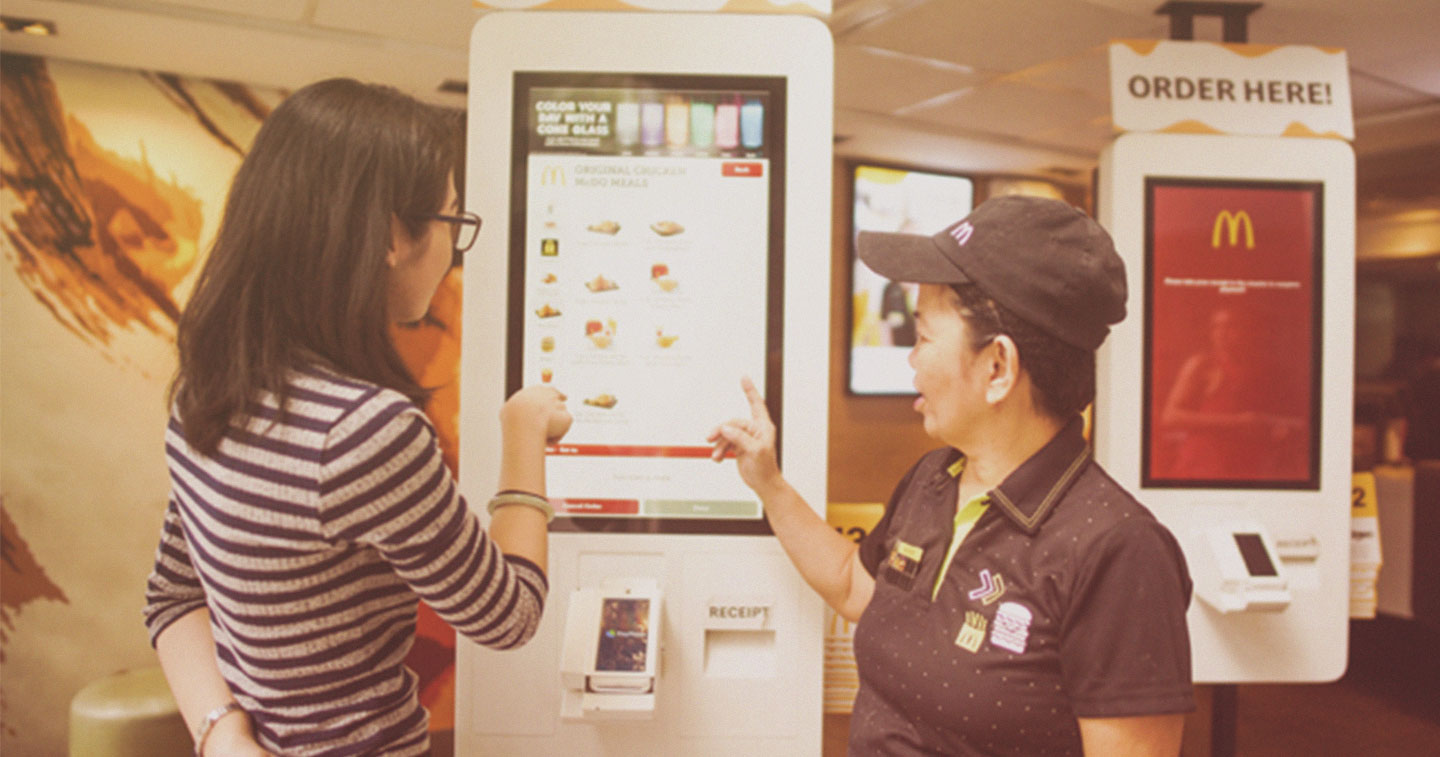

Source: Adobo Magazine
These technologies automate tasks like taking orders, processing payments, and managing inventory. Not only do they improve order accuracy and speedy service, they also reduce manual and tedious work which lets the staff focus on aspects of the work that require a human touch. This might include providing better customer service, ensuring the quality of the food, and creating a more welcoming dining experience. Although, this shift necessitates employees to adapt and acquire new skills related to technology, and can potentially lead to job displacement for routine tasks.
Retail
Self-checkout Counters
These automated systems allow customers to scan and pay for their purchases independently, reducing the need for cashiers. While this has reduced the demand for cashier positions, employees now have time freed up from transaction processing. This shift allows them to take on other responsibilities such as assisting customers, restocking shelves, and reorganizing merchandise.
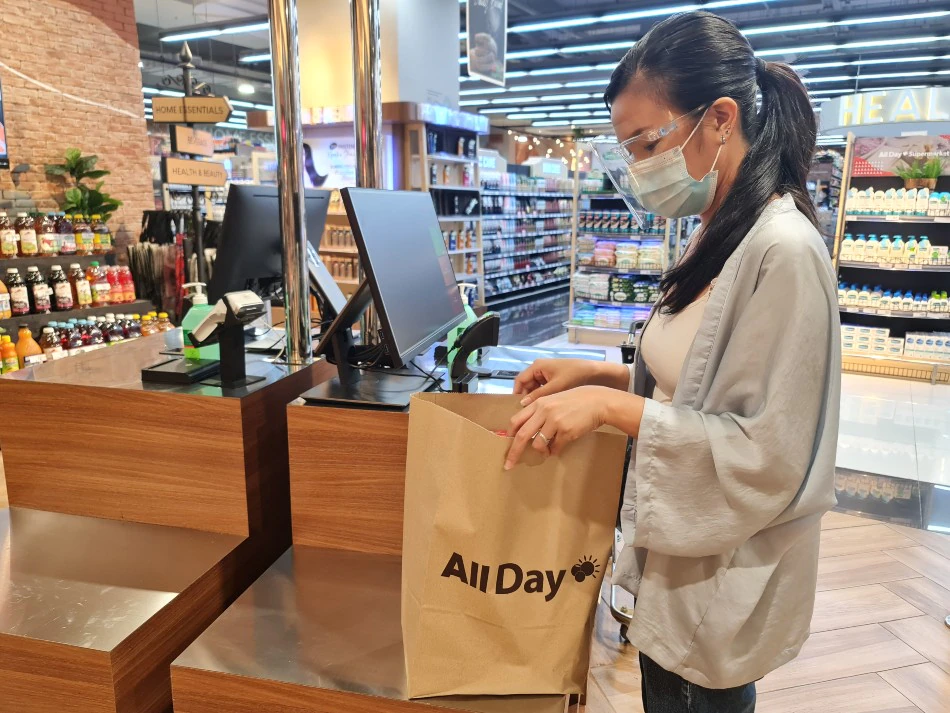

Source: ABS-CBN NEWS
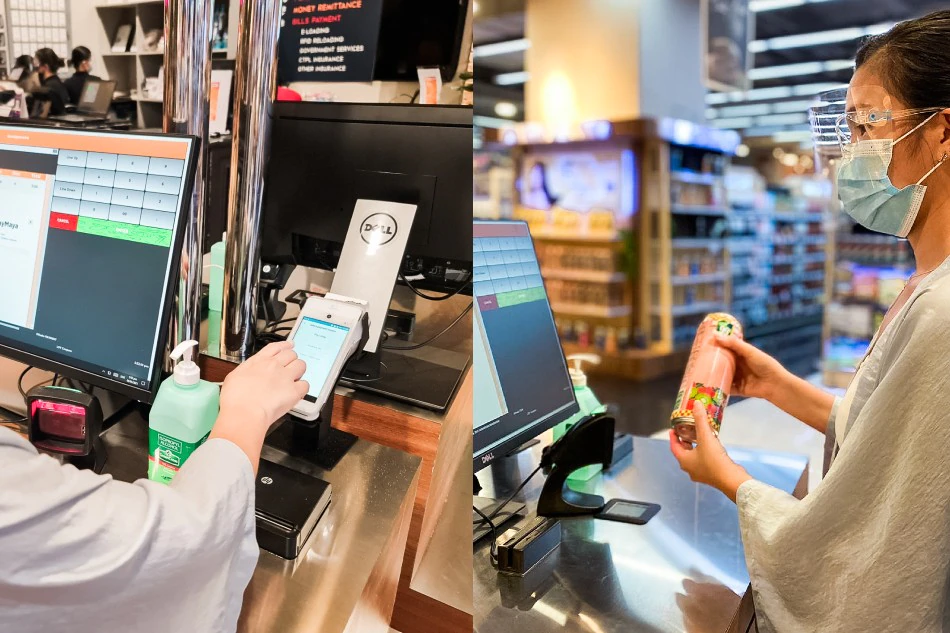

Source: ABS-CBN NEWS
Similar to food service, automation has streamlined various operational processes in the retail industry. The adoption of automation, however, also requires employees to adapt to new roles focused on customer assistance, technical support, and data interpretation.
Robotics
Robotics is effectively disruptive in the workforce, which extends to various sectors. Physical machines (robots) are created to do tasks of varying difficulties, originally performed by humans, whereas some noticeably improve beyond what a human could.
This field’s capabilities allow it to fit in with Clayton Christensen's theory of disruptive innovation, where its entry or adoption to industries brings transformative changes in the status quo of operational relationships between businesses, employers, and workers. The integration of ‘robots’ in workplaces has potentially and concurrently displaced human resources of organizations, business sectors, industries, or the economy.
Situations Where Robotics Disrupts The Workforce
Agriculture
Seeding
Mostly used in forestry industries, automated drone seeders help plant seeds in hard-to-reach areas and can help with replanting without putting farmers or workers in danger. They are capable of planting 400,000 trees a day with 2 operators and 10 drones.
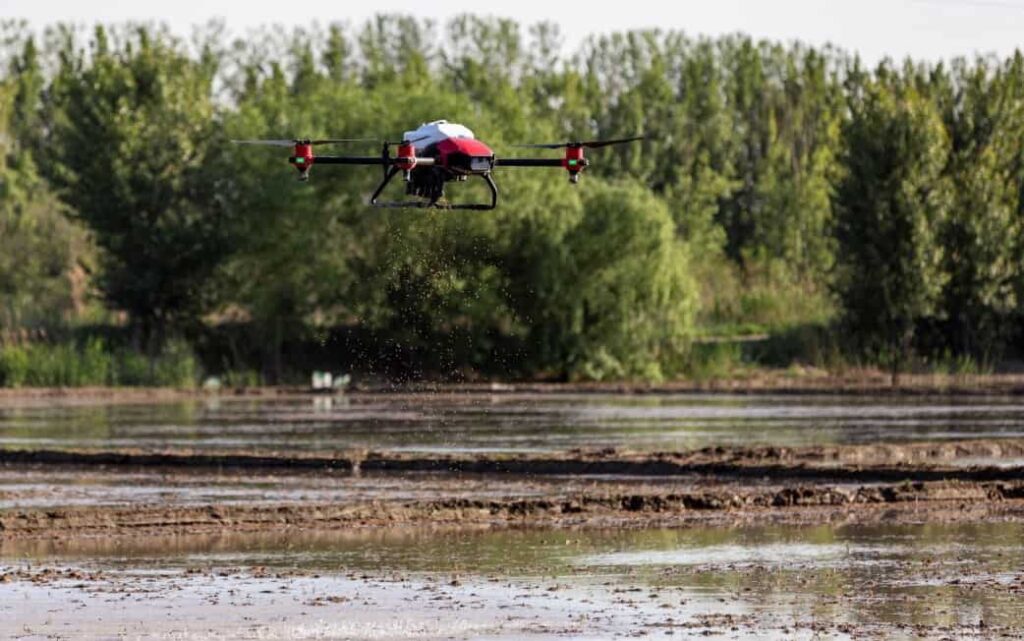

Source: Cision
Weeding
Weeds are the #1 enemy of farmers as they can harm crops and steal nutrients from crops, and in the long run also harm livestock. FarmWise, a San Francisco startup company, raised money to create a robot that helps deal with weeds while using an organic method. By using computer vision and several mechanical tools, the robot picks weeds out individually instead of using chemicals.

Source: Croptracker
In Australia, researchers from the University of Western Australia and the University of Sydney have created a weeding machine called "weed-chipper" which uses tines to break up weeds that are detected by the camera.

Source: Croptracker
Robotic Harvesting
Robots can change the future of harvesting and work alongside farmers to help pick fruits and other plants during harvest. The goal is not to replace humans but to allow 24-hour harvesting.
.jpg)
Source: #HowToRobot
Healthcare
Surgery
-
• da Vinci Surgical Robot: This robot is a system that doctors control to make precise incisions using a magnified 3D HS vision and controls. It helps make incisions that the doctor's hands may not be able to make and it is less invasive and offers faster healing time for patients.
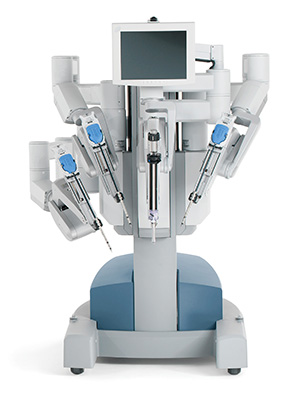
Source: UC Health
-
• The CyberKnife: This is not an actual knife, but a robot that helps with radiation therapy most commonly used to treat cancer at hospitals and treatment centers. It repositions itself to help target multiple angles without having to move the patient to different positions, is non-invasive, and helps minimize exposure of healthy organs to radiation.
.jpg)
Source: UCSF Health
Sanitation
-
• Xenex Germ-Zapping Robot: Hospital-acquired infections are a big problem in healthcare that could be improved by robots. The Xenex is a robot that can disinfect hospital rooms in minutes using UV rays that kill a range of infectious bacteria.

Source: Woman's
Therapy
-
• PARO Therapeutic Robot: This is an interactive device, close to animal therapy without depending on actual animals that helps patients find comfort, reduce stress, and help with recovery of patients with mental illnesses or patients that just came from surgery.
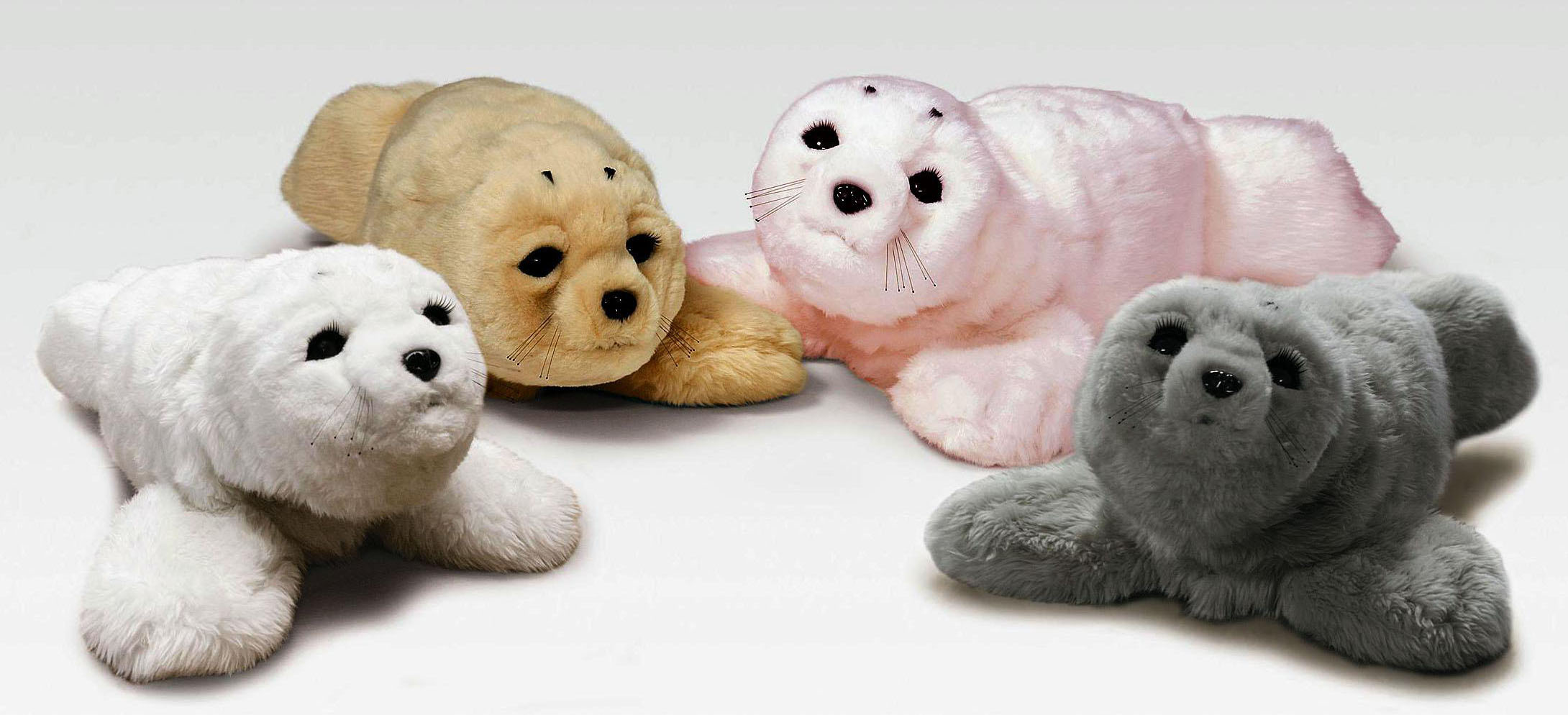

Source: TheJapanTimes
Warehousing
-
• Automated Guided Vehicles: AGVs are the replacement of manually-driven forklifts and carts. They navigate through the warehouse by following wires, tracks, sensors, and magnetic strips on the floor to create a route.
.jpg)
Source: DMMetal
-
• Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems: AS/RS helps automate inventory management and store goods on demand. They are used to help speed up completing orders and handling materials.
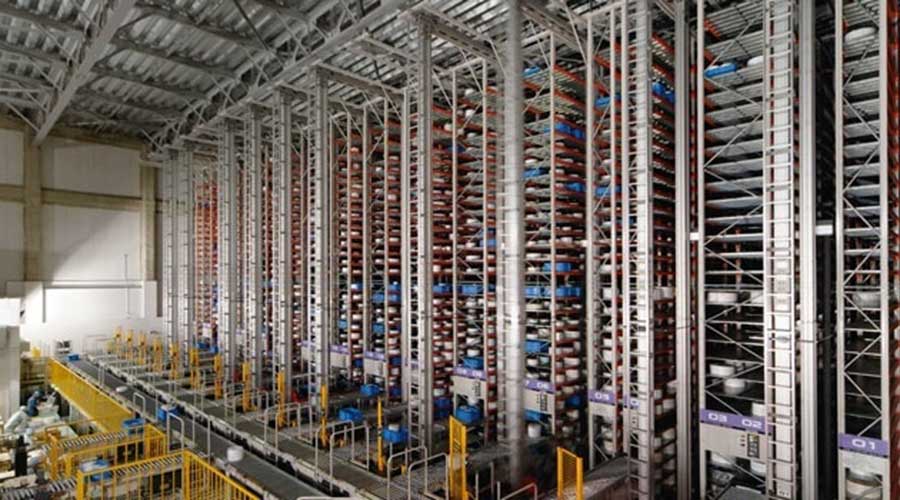

Source: Storage Solutions
Advantages and Disadvantages in the Workforce
From the examples provided above, we get a glimpse into how automation and robotics have significantly improved the way humans do things. The main goal of these innovations is to improve our quality of life by streamlining processes and making jobs easier and more efficient. At the same time, however, they also pose certain disadvantages which shows that they are not perfect systems. Below are some of the pros and cons of automation and robotics.
ADVANTAGES
Increased efficiency, productivity, and accuracy
Automation and robotics are used in different industries and operations today as they enhance productivity by increasing production output at a faster speed. By reducing manual labor, these automated systems also eliminate human error which leads to output that is standard and passes quality control.

Source: Canning Line
Cost-efficiency
Automation and robotics allow companies to save money by reducing labor costs and streamlining processes. With the need to hire human workers reduced, companies are able to allocate their resources more efficiently. Instead of having to pay employees' salaries, they can allot the budget into investments for additional hardware/software or upgrading them.
Increased workplace safety
By reducing the need for manual labor, automation can reduce work-related injuries and accidents, especially in dangerous roles and/or in hazardous work environments.
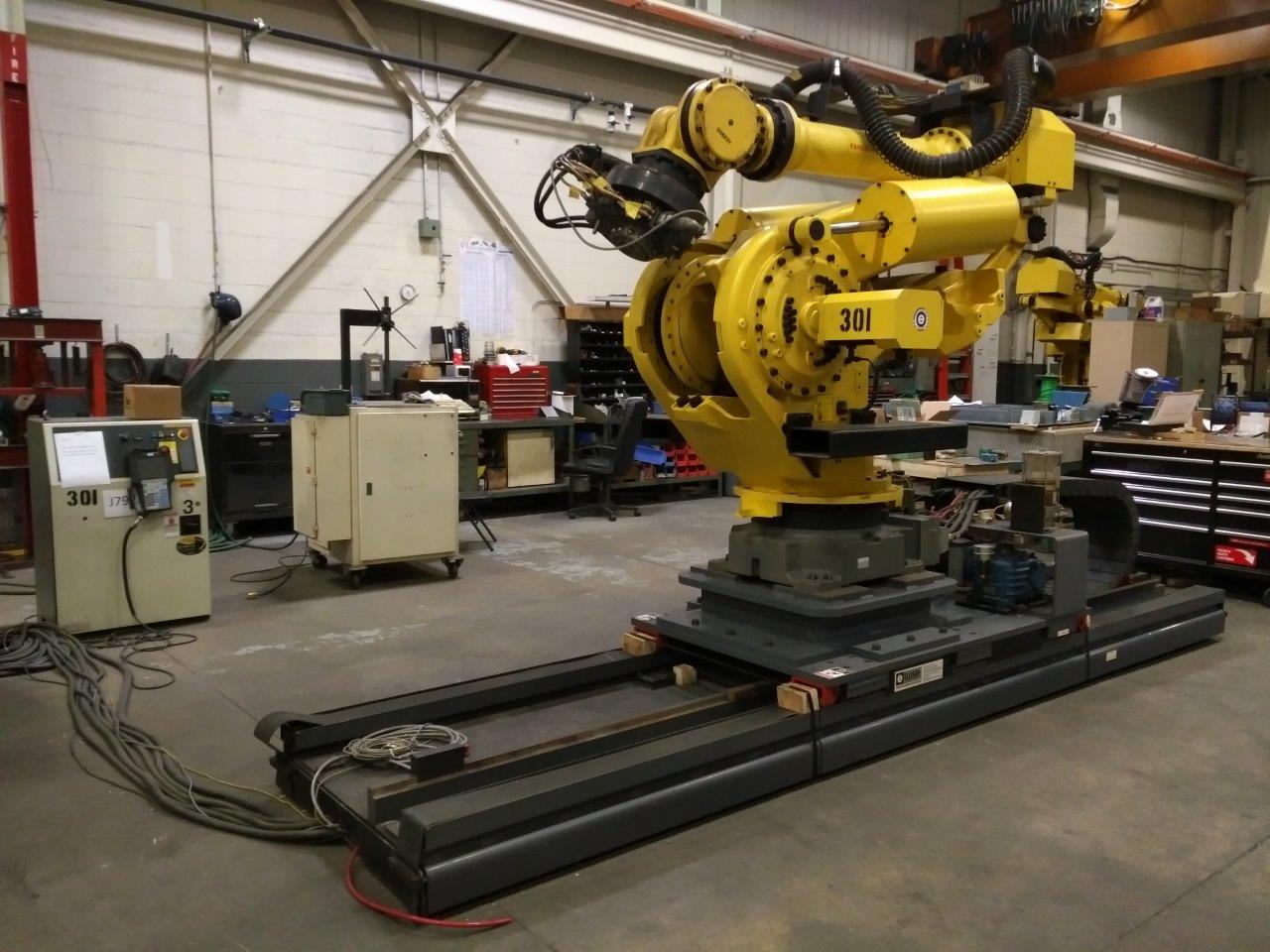

Source: Heavy Payload Robots
One of the most common uses of robotics and automation in the industry is the use of heavy payload robots. These are pieces of machinery that can lift objects weighing over 200 kilograms. By utilizing these, human workers no longer need to manually perform the heavy lifting tasks which may result in physical injuries.
DISADVANTAGES
One of the major concerns that most people have against automation and robotics is that they are going to replace humans. A lot of movies associate these technologies with dystopian futures, further adding to the public's apprehension against them. Although we as a society haven't reached an alarming point technology-wise, we can't deny that we are beginning to see that this kind of fear has a certain validity to them. Below are examples of the disadvantages and limitations of automation and robotics.
Job displacement and unemployment
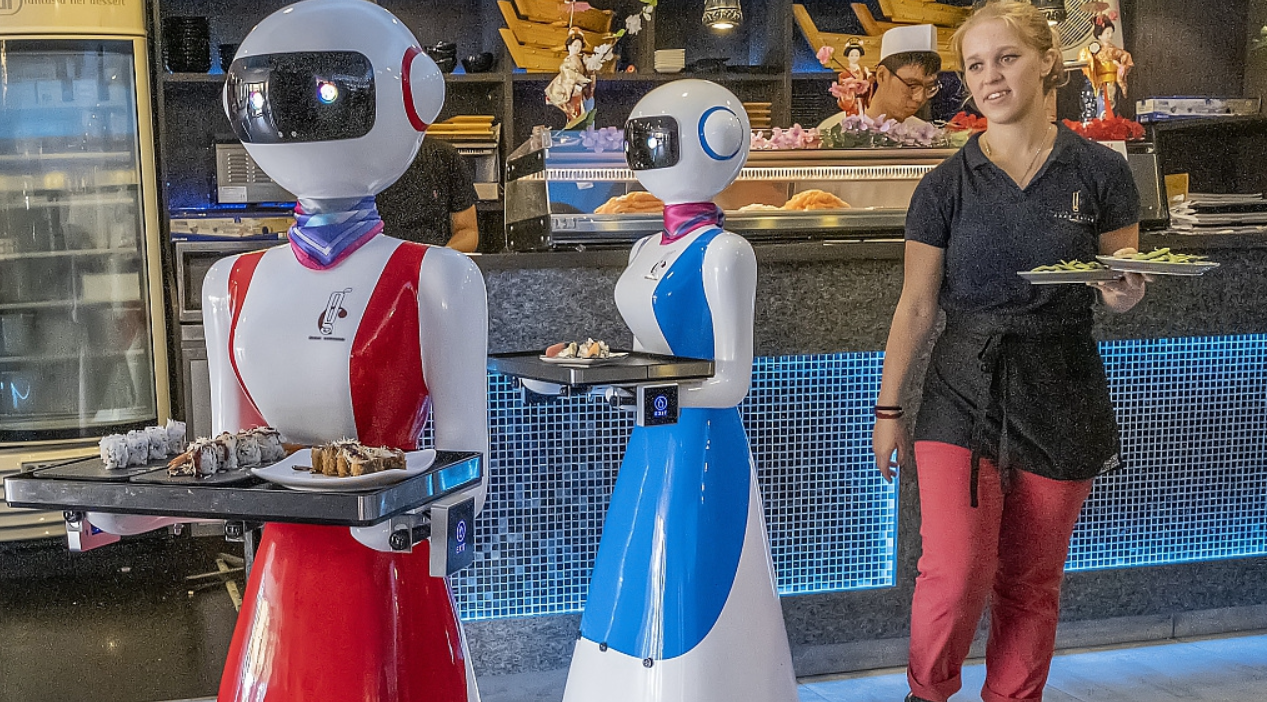
More and more companies utilize automation and robotics today, reducing the need for human workers. This can potentially lead to job loss and increase the unemployment rate. Let’s take a look at Jollibee, for example. Since 2022, Jollibots have been in use in several stores nationwide. These adorable robots assist with bringing customers‘ orders directly to their tables. Once an order is ready to be dispatched, a crew member only needs to place the meal tray onto a Jollibot, and the robot will “look” for the correct table by scanning the area for the tracker that the customer was provided after they placed and paid for their order. Once the right table is identified, the Jollibot will approach it and the customer may then take their meal tray and return the tracker to the Jollibot.
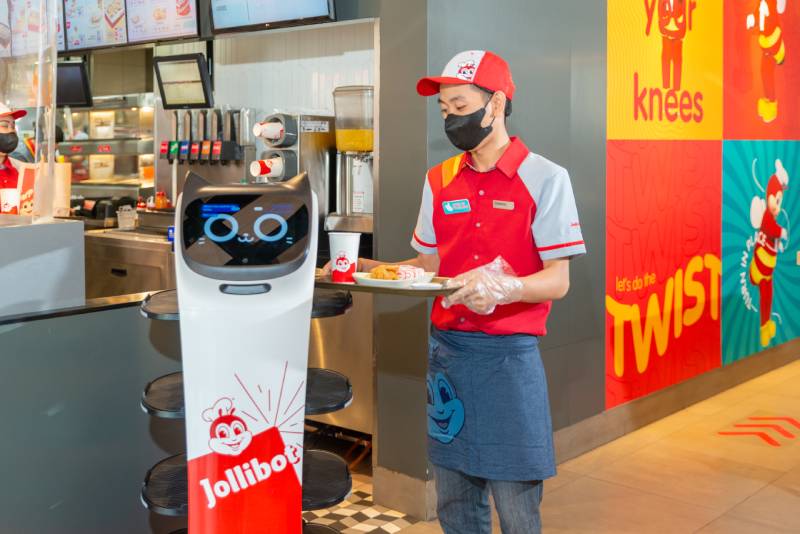

Source: Jollibots
From a business perspective, Jollibots are a great innovation. Most of us have been to Jollibee during lunch or dinner rush and we’ve seen how chaotic it can be. With the use of Jollibots, dispatching orders is one of the repetitive tasks taken off service crew members’ hands, allowing them to do other tasks. Jollibots also reduce the risk of accidental spilling or dropping of food trays which can happen with manual food service. Jollibots help the company serve its customers more efficiently, but they also lead to a reduced need for staff members.
High implementation and maintenance costs
To reap the cost-efficiency benefits that automation and robotics provide in the long run, companies may need to shell out a huge amount of money to purchase automated systems and their software, as well as train their employees as they incorporate automation into their workflows. Automated systems also require regular maintenance to ensure smooth operation. In cases of technical failures, repair may also be costly.
Reduced human interaction and customer experience
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to the rise of telemedicine and the use of other healthcare technologies. They have allowed patient care to be easier and virtually accessible.

Source: Konsulta MD
While automation and robotics provide a certain level of efficiency, it can't replace some services that only the human touch can provide, such as empathy and complex decision-making. Some patients, especially older ones, may also be hesitant to use automated systems for lack of familiarity with new technology and may prefer talking to an actual human/doctor.
Skill loss and dependency to technology
People used to be able to perform arithmetic calculations manually or mentally with ease, but with the rise of computers/calculators, added with faster processing speed offered by automation, most of us are no longer able to do it as easily as we used to. Farming also used to be a much simpler task as everything used to be done manually. Robotics has definitely helped with agriculture, but it can also lead to humans forgetting how to plant and maintain crops without the aid of technology.
As we replace repetitive, lower-skilled jobs, we also run the risk of losing human skills and expertise. Automation and robotics can result in humans being so reliant on technology that we forget or find it hard to perform certain tasks without automated systems.
Conclusion
In summary, we have concluded that technology has been rapidly developing and focused the discussion on two types of technology: automation and robotics, and their roles in reshaping the workforce. After explaining and clarifying the definitions and examples of the terms, we have deduced that these technologies, when used professionally for businesses that provide services or products, indeed offer various advantages, although they still have their downsides. Nonetheless, it is undeniable that they critically affect how businesses move forward and establish their production and operating systems, particularly regarding how they utilize and redesignate their employees in their organization or enterprise.
References
- 5 Medical robots making a difference in healthcare. (2001, October 13). CWRU Online Engineering. https://online-engineering.case.edu/blog/medical-robots-making-a-difference
- Adobo Magazine. (2020, February 26). [McDonald’s staff and customer demonstrating their self service kiosk]. .. https://www.adobomagazine.com/press-release/brand-business-mcdonalds-philippines-sustains-double-digit-growth-with-innovations-driving-enhanced-customer-experience/
- Ahmed, M. (2022, April 7). Top Advantages of Online Assessment Tools in Education. MasterSoft. https://www.iitms.co.in/blog/top-advantages-of-online-assessment-tools.html
- AllHome AllDay Supermarket. (2021, May 17). This supermarket introduces self-checkout counter. ABS-CBN News. https://news.abs-cbn.com/advertorial/life/05/17/21/this-supermarket-introduces-self-checkout-counter
- Automated welding using industrial robots. (n.d.). Wevolver. https://www.wevolver.com/article/robots-in-the-manufacturing-industry-types-and-applications